
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
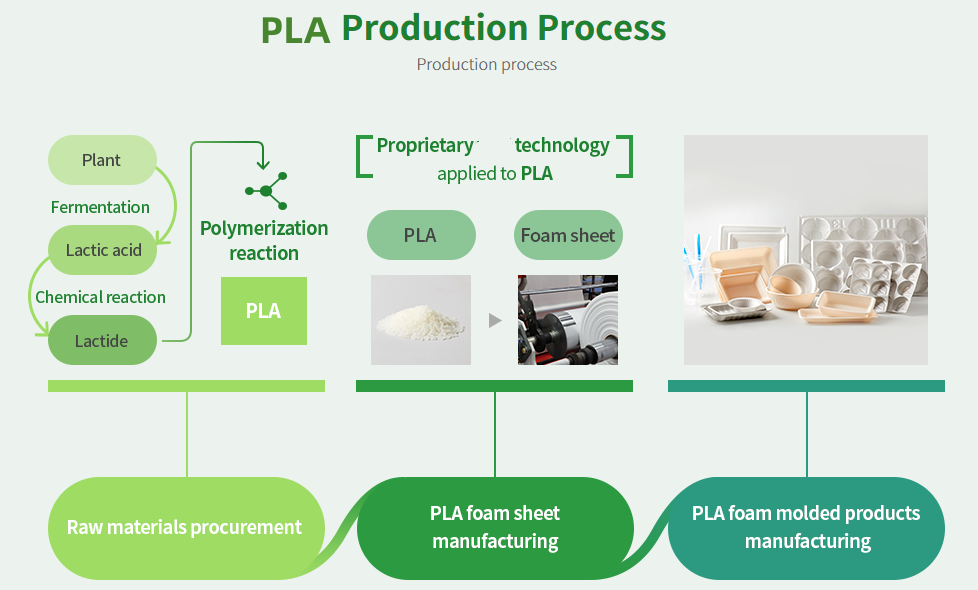
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable and renewable polymer derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. PLA membrane films have gained significant attention in various industries due to their excellent barrier properties, biodegradability, and compatibility with food packaging applications. Here is an overview of the development process for PLA membrane films:
1. Raw Material Selection: The first step in developing PLA membrane films is selecting the appropriate raw material, which is typically PLA resin. The resin's molecular weight, crystallinity, and thermal properties are crucial factors influencing the film's performance.
2. Film Formation: PLA membrane films can be produced using various methods, including melt extrusion, solvent casting, and solution casting. Melt extrusion involves melting the PLA resin and extruding it through a die to form a continuous film. Solvent casting involves dissolving the PLA resin in a suitable solvent and casting it onto a substrate, followed by solvent evaporation. Solution casting is similar to solvent casting but involves the formation of a solution before casting.
3. Film Processing: After film formation, various processing techniques can be employed to enhance the film's properties. These techniques include stretching, annealing, and surface modification. Stretching the film in both the machine and transverse directions improves its mechanical strength and barrier properties. Annealing, which involves heating the film to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling it, enhances its crystallinity and thermal stability. Surface modification techniques like corona treatment or plasma treatment can improve the film's wettability and adhesion.
4. Characterization: PLA membrane films need to be thoroughly characterized to ensure they meet the desired specifications. Common characterization techniques include measuring film thickness, mechanical properties (tensile strength, elongation at break), thermal properties (melting temperature, glass transition temperature), barrier properties (water vapor transmission rate, oxygen transmission rate), and surface properties (contact angle, surface energy).
5. Optimization: The development process often involves iterative optimization to achieve the desired film properties. Factors like processing parameters, raw material composition, and additives can be modified to optimize the film's performance.
6. Applications: Once the PLA membrane film is developed and optimized, it can be used in various applications such as food packaging, biomedical devices, agricultural films, and water purification membranes.

Mr. Liu
Tel:
86-0533-2802680
Fax:
86-0533-2802680
E-mail:
Related Products List
Mobile Site


Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.